Trademark licensing involves granting permission to another party (the licensee) to use a trademark owned by the licensor under specific terms and conditions. These agreements are common in various industries, including fashion, entertainment, technology, and franchising. They allow licensors to generate revenue from their trademarks while enabling licensees to benefit from the established brand value.
However, managing trademark licenses can be challenging. It involves monitoring the use of the trademark to ensure compliance with quality standards, calculating and collecting royalties, and addressing potential breaches or disputes. The traditional processes for managing these tasks are often time-consuming, expensive, and prone to human error.
The Role of Smart Contracts in Trademark Licensing
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They operate on blockchain platforms, which are decentralized, immutable ledgers that record transactions in a secure and transparent manner. Smart contracts can automatically enforce the terms of a contract without the need for intermediaries, reducing the potential for disputes and increasing efficiency.
When applied to trademark licensing, smart contracts offer several significant advantages:
- Automation of Contract Execution: Smart contracts can automate many aspects of trademark licensing agreements. For example, they can automatically trigger royalty payments when certain conditions are met, such as sales targets or usage milestones. This reduces the need for manual calculations and minimizes the risk of errors. It also ensures that both parties fulfill their obligations promptly, as the contract terms are enforced automatically.
- Enhanced Security and Trust: Blockchain technology provides a high level of security due to its decentralized and immutable nature. Once a smart contract is deployed on a blockchain, it cannot be altered without the consensus of the network participants. This ensures that the terms of the trademark licensing agreement are secure and tamper-proof, building trust between the licensor and licensee.
- Transparency and Accountability: All transactions and contract executions on a blockchain are recorded in a transparent and traceable manner. This means that both licensors and licensees can access a verifiable record of all activities related to the trademark license, from the issuance of the license to the payment of royalties. This transparency reduces the likelihood of disputes and makes it easier to resolve any issues that may arise.
- Streamlined Royalty Payments: One of the most significant pain points in trademark licensing is the calculation and distribution of royalties. Smart contracts can automatically calculate royalties based on predefined criteria, such as the number of units sold or revenue generated. These payments can be made instantly in cryptocurrencies or traditional currencies, depending on the agreement, reducing delays and ensuring timely compensation for the licensor.
- Efficient Dispute Resolution: Smart contracts can also include automated dispute resolution mechanisms. For instance, if there is a disagreement over whether a trademark has been used according to the agreed terms, the smart contract can refer the dispute to an independent arbitrator or use predefined criteria to make a determination. This reduces the need for lengthy and costly legal proceedings.
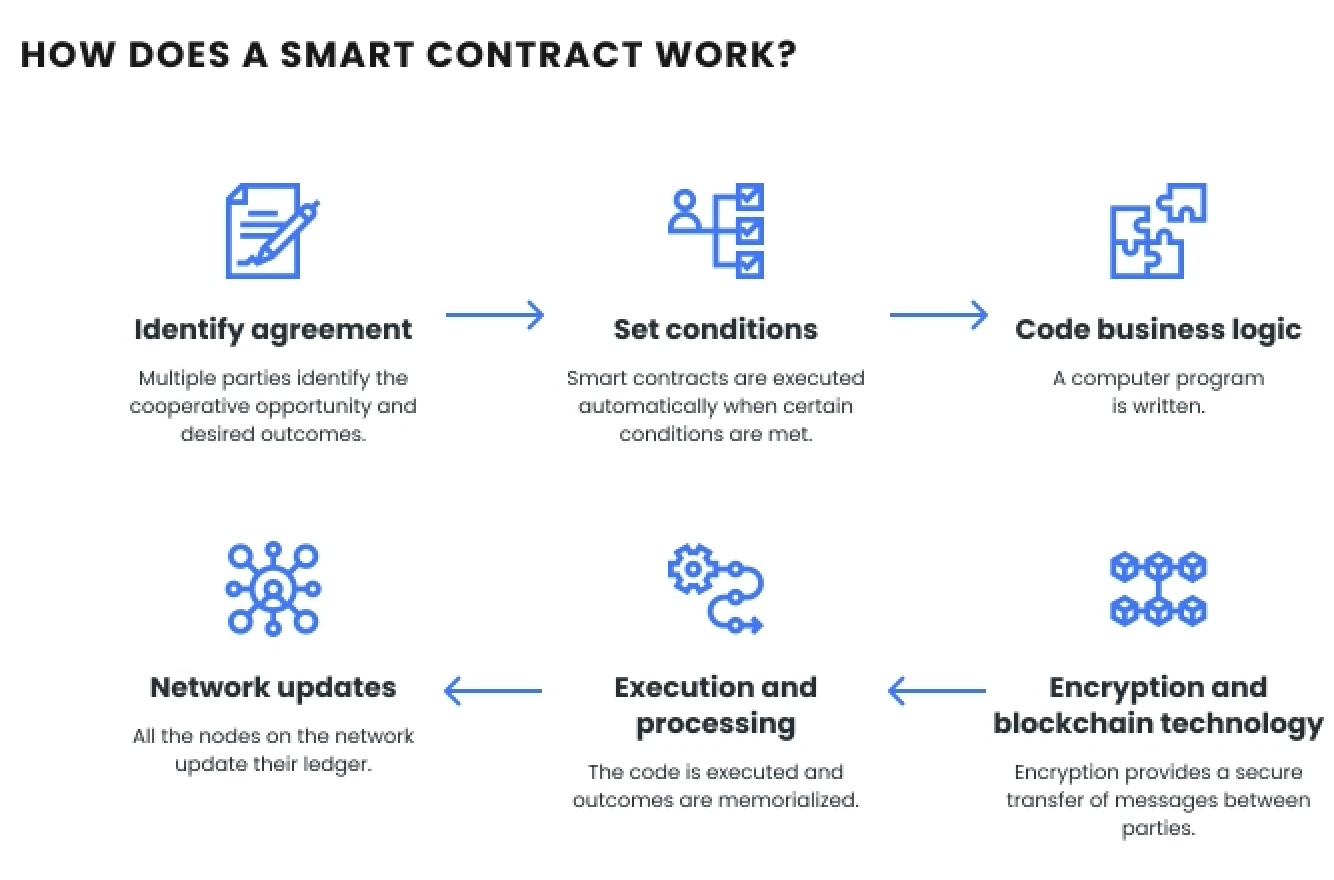
Implementing Smart Contracts for Trademark Licensing
While the benefits of smart contracts in trademark licensing are clear, their implementation requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Legal Recognition and Compliance: The legal status of smart contracts varies across jurisdictions. For smart contracts to be effective in trademark licensing, they must be recognized as legally binding agreements. This requires alignment with existing IP laws and regulations. Businesses looking to adopt smart contracts must ensure that their contracts comply with local legal requirements and are enforceable in court.
- Smart Contract Design: The effectiveness of a smart contract depends on how well it is designed. The contract must clearly define all terms and conditions, including usage rights, quality standards, royalty calculations, and dispute resolution mechanisms. Additionally, the code must be thoroughly tested to ensure that it operates as intended and does not contain vulnerabilities that could be exploited.
- Interoperability with Existing Systems: To fully realize the benefits of smart contracts, they must be able to integrate with existing business systems, such as sales tracking, inventory management, and financial accounting. This may require the development of custom interfaces or the adoption of compatible blockchain platforms that can work seamlessly with traditional systems.
- Education and Adoption: As with any new technology, the successful adoption of smart contracts for trademark licensing will depend on educating stakeholders about their benefits and how to use them effectively. This includes training for legal professionals, IP managers, and business executives, as well as fostering a broader understanding of blockchain technology.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite their potential, the widespread adoption of smart contracts in trademark licensing faces several challenges:
- Complexity of Licensing Agreements: Trademark licensing agreements can be complex, involving multiple parties, jurisdictions, and contingencies. Translating these intricate legal documents into code that can be executed by a smart contract is a significant challenge that requires collaboration between legal experts and software developers.
- Technological Barriers: While blockchain technology is rapidly advancing, it is still relatively new and may not yet be capable of handling the full scope of trademark licensing activities. Issues such as scalability, transaction speed, and energy consumption need to be addressed to make smart contracts a viable solution for large-scale IP management.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory landscape for blockchain and smart contracts is still evolving. Governments and regulatory bodies are in the process of developing frameworks to govern the use of these technologies. Businesses must navigate this uncertain environment while ensuring that their use of smart contracts remains compliant with existing laws.
Looking ahead, the future of smart contracts in trademark licensing appears promising. As blockchain technology matures and becomes more widely adopted, smart contracts have the potential to become a standard tool for managing IP rights. Innovations such as decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) could further enhance the way trademark licensing agreements are created, managed, and enforced.
Conclusion
Smart contracts on blockchain platforms represent a significant innovation in the field of trademark licensing. By automating and securing licensing agreements, smart contracts offer a more efficient, transparent, and reliable way to manage trademark rights. While challenges remain, the potential benefits of this technology are substantial, making it an exciting area of exploration for businesses looking to protect and leverage their intellectual property in the digital age. As blockchain and smart contract technologies continue to evolve, they are likely to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of trademark licensing and IP management.
